The flourishing market of nanocomposite food packaging has raised concerns about the safety of these materials. While several works on this issue have been published in recent years, they main focus in these studies was found to be on the possible migration of the nanoparticle its constituents.
Read MoreThis Special Issue is open to valuable contributions presenting advances on the elucidation of the potential toxic effects of nanoparticles. For years, humans have been exposed—intentionally or unintentionally—to a broad range of nanoparticle-containing products.
Read MoreCellulose nanocrystals (CNC) and xyloglucan (XG) were used to construct new aerogels inspired by the hierarchical organization of wood tissue, i.e., anisotropic porous cellular solid with pore walls containing oriented and stiff cellulose nanorods embedded in hemicellulose matrix.
Read More‘HOT articles’ are articles which have receive particularly high scores at peer review.
Read MoreDespite considerable research effort devoted to the study of the effects of silver nanoparticles on mammalian cells in recent years, data on the potential long term effects of this nanomaterial remain scarce, and centered on epithelial cells.
Read MoreThe COVID-19 outbreak has fueled a global demand for effective diagnosis and treatment as well as mitigation of the spread of infection, all through large-scale approaches such as specific alternative antiviral methods and classical disinfection protocols.
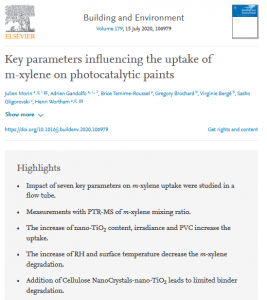
Read MoreGiven the toxic nature of many volatile organic compounds (VOCs) present within indoor environments, it is necessary to develop new materials to eliminate them. Photocatalytic paints represent a promising technology to remove the indoor pollutants but they are not optimised yet.
Read MoreThe impact on human health of long-term exposure to low doses of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) remains understudied.
Read MoreThe vast diversity of applications using nanomaterials and enhanced physicochemical properties at the nanoscale have raised questions concerning their potential environmental risks. Assessing the risk of nanomaterials in a real ecosystem is extremely challenging because of the system complexity and the relevant environmental doses tested.
Read MoreNew article by Carriere et al. in Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis
TiO2 particles are broadly used in daily products, including cosmetics for their UV-absorbing property, food for their white colouring property, water and air purification systems, self-cleaning surfaces and photoconversion electrical devices for their photocatalytic properties.
Read More