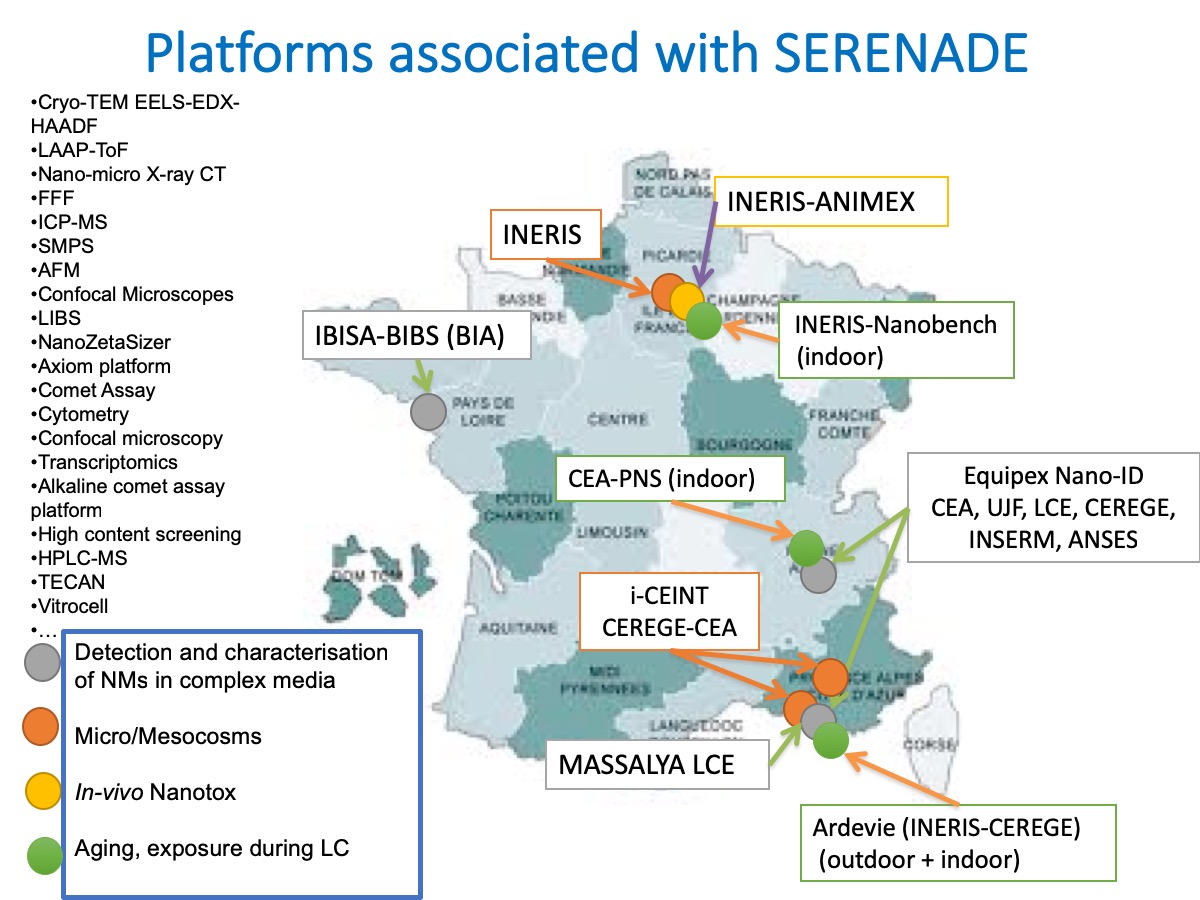
Platforms associated with SERENADE
Expertise
You can find a list of the main platforms and tools associated with the Labex SERENADEDo not hesitate to contact us for more informations on the tools and technics.
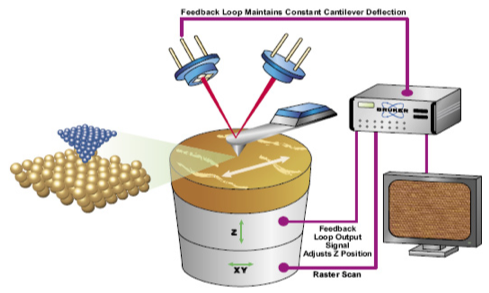
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
Atomic Force Microscopy is a very high-resolution device which provides 3D profile of a surface at nanometric scaleThis technique deals with the measure of different forces (mainly van der waals forces) between a tip (probe) supported on a flexible cantilever, and the surface at very short distance.

Comet assay
The Single Cell Gel Electrophoresis assay (also known as comet assay) is a sensitive technique for the detection of DNA damage at the level of the individual eukaryotic cell.The principle is based upon the ability of denatured cleaved DNA fragments to migrate out of the cell under the influence of an electric potential (the "comet tail"), whereas undamaged supercoiled DNA remains (the "comet head") when a current is applied.
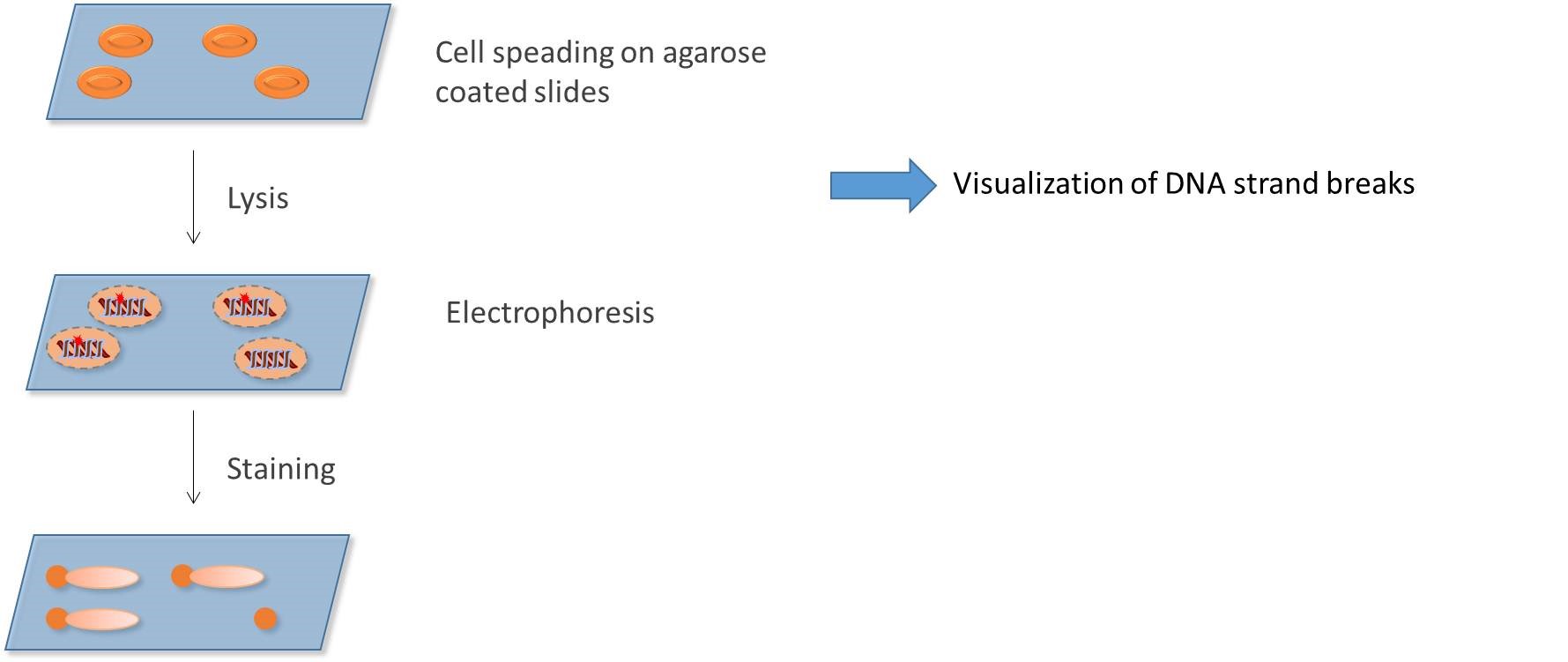
Alkaline comet assay platform
The comet assay is a rapid and sensitive test allowing the detection of DNA damage, such as single and double-strand breaks, as well as alkali-labile sites, in eukaryotic cells.It is based on the ability of negatively charged loops/fragments of DNA to be drawn through an agarose gel in response to an electric field.
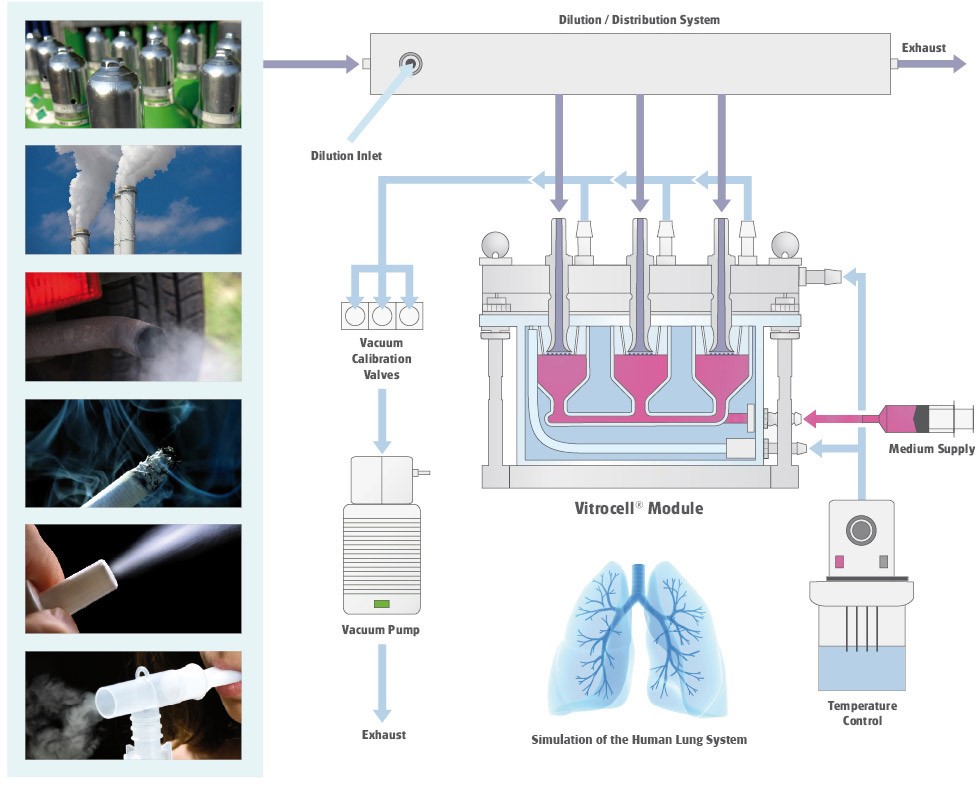
Air Liquid Interface exposure to nanomaterials
VITROCELL®'s systems have been specifically designed and engineered to enable direct exposure of mammalian cells or tissue at the air/liquid interface where the cell systems are not covered with culture medium.All cell types cultivated on microporous membranes can be used.
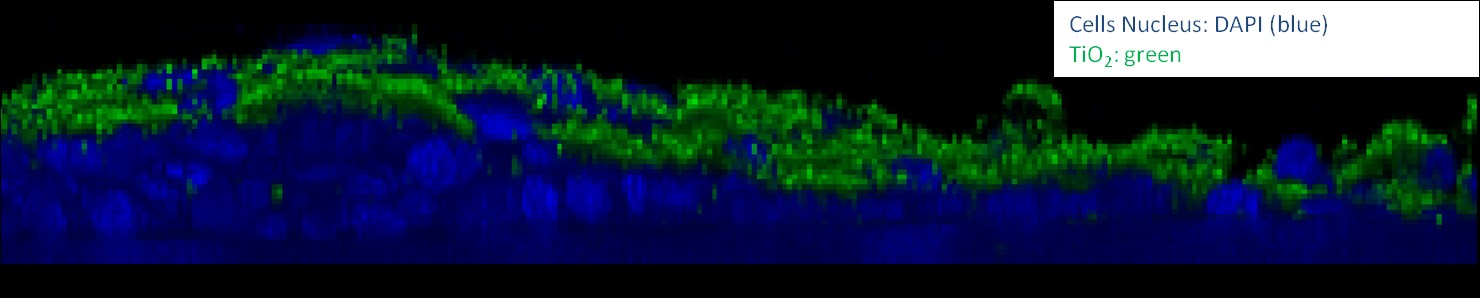
Confocal microscopy
Confocal microscopy is an optical imaging technique.It enables the reconstruction of three-dimensional structure from the obtained images.
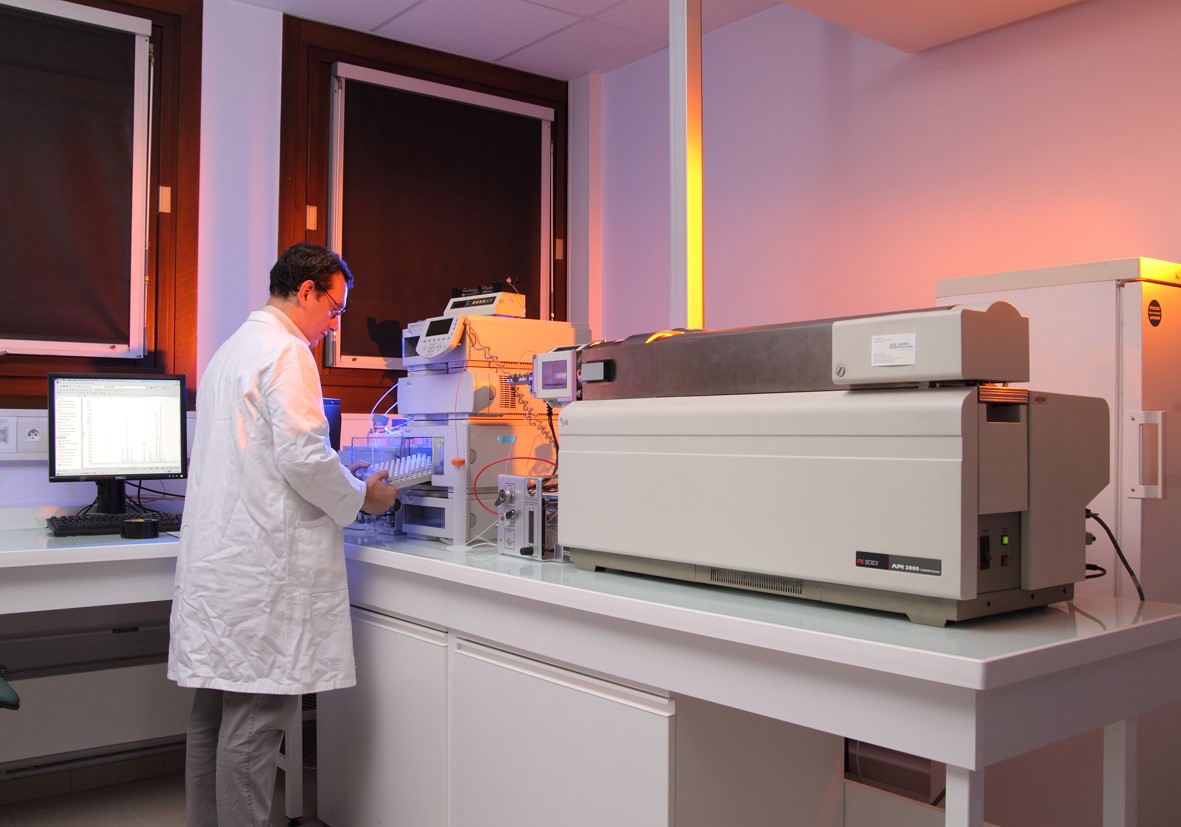

Liquid chromatographycoupled to tandem mass spectrometry
HPLC-MS/MS is an analytical chemistry technique that combines the physical separation capabilities of liquid chromatography (or HPLC) with the mass analysis capabilities of mass spectrometry.This technique allows identification, quantitation and mass analysis of samples.
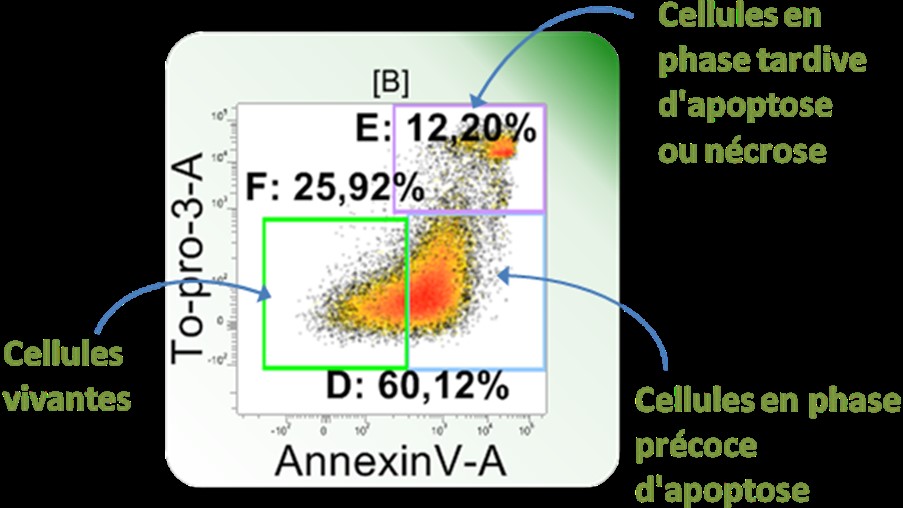
Cytometry
The basic principle of flow cytometry is the passage of cells in single file in front of a laser so they can be detected and counted.Cell components are fluorescently labelled and then excited by the laser to emit light at varying wavelengths.
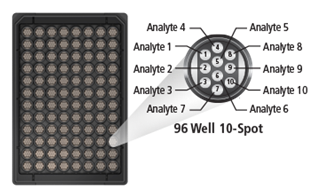
ELISA multi-array
MULTI-ARRAY technology combines electrochemiluminescence and arrays to bring speed and high density of information to biological assays.In combination with MULTI-SPOT plates, this technology enables precise quantitation of multiple analytes in a single sample requiring less time and effort than other assay platforms.

High content screening
Analytical methods using automated microscopy, multi-parameter image processing, and visualization tools to extract quantitative data from cell populations.HCS typically employs fluorescence imaging of samples in a high-throughput format and reports quantitatively on parameters such as spatial distribution of targets and individual cell and organelle morphology samples.

Dynamic light scattering
ZetaSizer (Nano-ZS) + Titrator MPT-2 (Malvern)The equipment is dedicated to the determination of the hydrodynamic diameters of spherical particles in aqueous suspensions (the principle of dynamic light scattering) and of the surface charge of these particles (zeta potential).
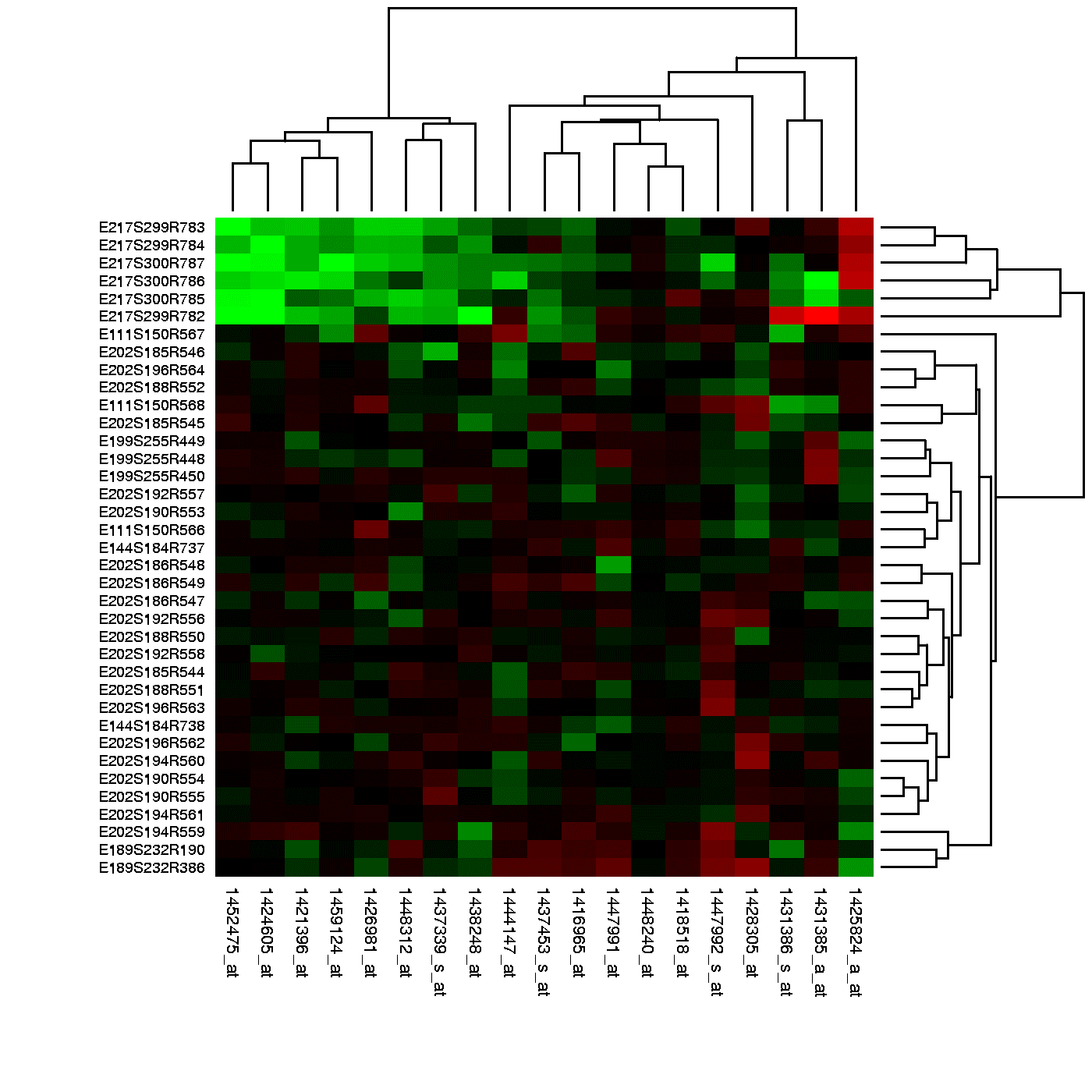
Transcriptomics
The transcriptome is the complete set of RNA transcripts that are produced by the genome, under specific circumstances or in a specific cell.Transcriptomics is the study of the transcriptome using high-throughput methods, such as microarray analysis.
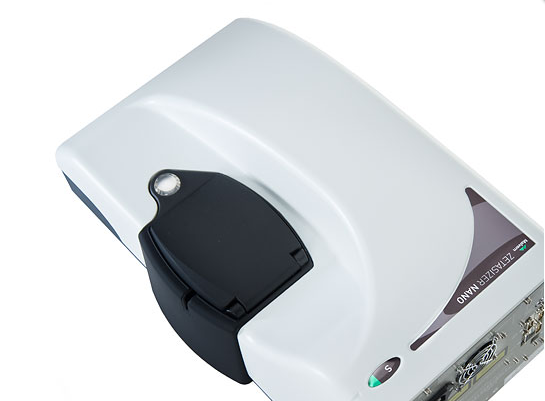

ZetaNano ZS
The Zetasizer Nano S is a research grade dynamic light scattering system for sub-micron particle and molecular size and molecular weight measurement that combines performance and versatility with exceptional ease of use.The system can be upgraded to add zeta potential capability at a later date.
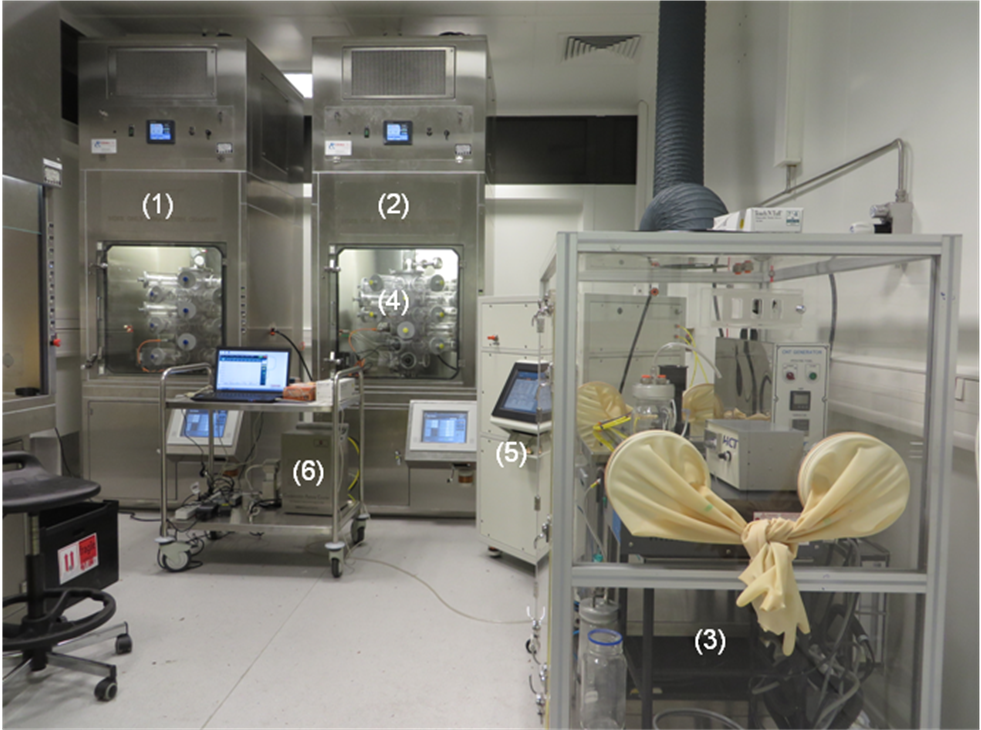

In vivo inhalation system
Nanoparticles nose-only inhalation system for rats
Axiom platform
Within MetaToul platform, AXIOM is in charge of the xenobiotic metabolism activity. It has leading equipment devoted to the development of projects in the field of food toxicology.This mainly includes instruments of mass spectrometry, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and their associated techniques of sample purification and separation.
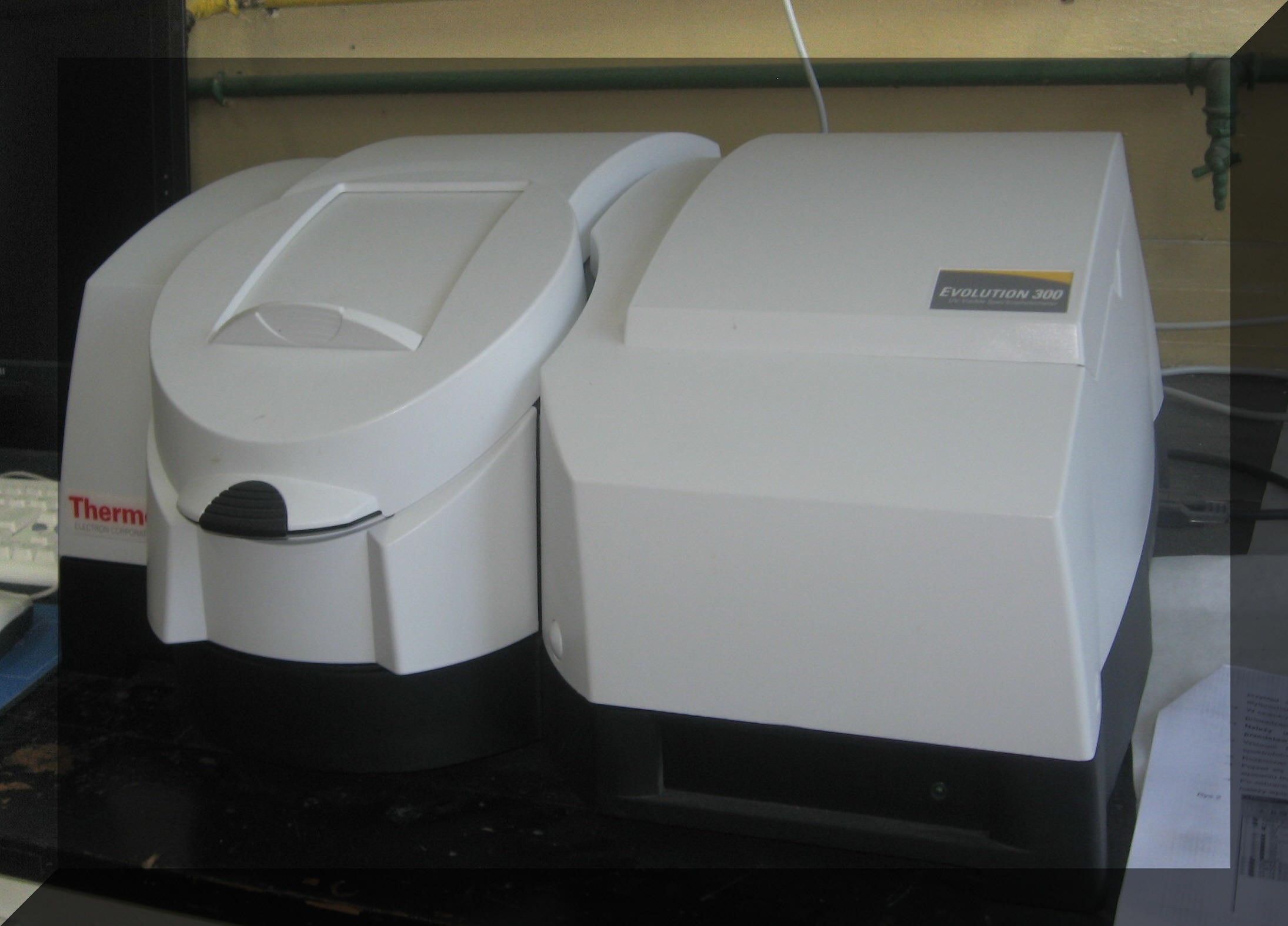

Ultra violet-visible spectroscopy
UV-vis spectroscopy refers to absorption spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region.This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared) ranges.
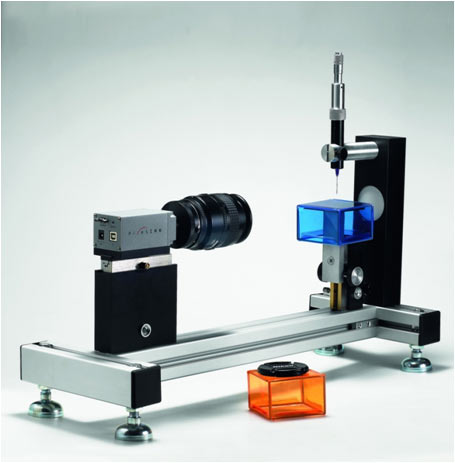

Contact angle
Measuring surface energy and wettability using contact sessile drop methodThe contact angle is the angle, conventionally measured through the liquid, where a liquid/vapour interface meets a solid surface.
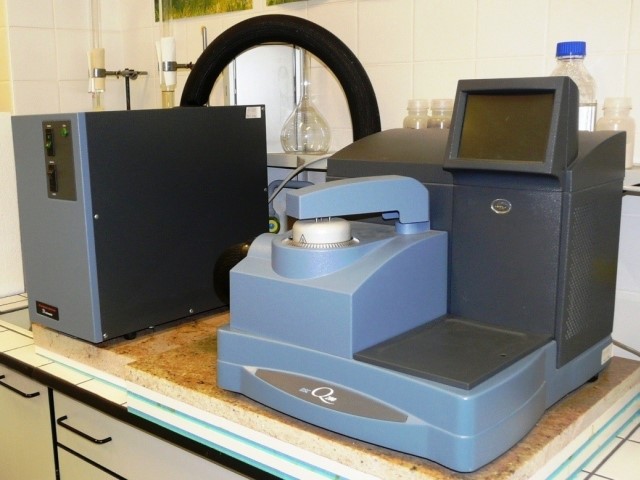

Differential Scanning Calorimetry
DSC is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is measured as a function of temperature.When the sample undergoes a physical transformation such as phase transitions, more or less heat will need to flow to it than the reference to maintain both at the same temperature.
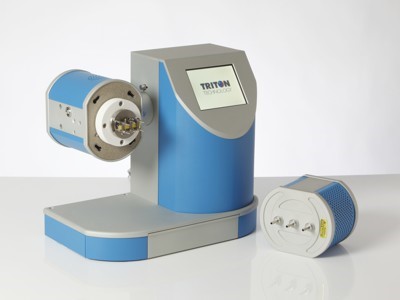
Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
DMA is a technique used to study and characterize materials. It is most useful for studying the viscoelastic behavior of polymers.A sinusoidal stress is applied and the strain in the material is measured, allowing one to determine the complex modulus.

Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is a technique which is used to obtain an infrared spectrum of absorption, emission, photoconductivity or Raman scattering of a solid, liquid or gas.An FTIR spectrometer simultaneously collects high spectral resolution data over a wide spectral range.

Gas chromatography
Gas chromatography is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition.Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, or separating the different components of a mixture (the relative amounts of such components can also be determined).

Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy is a scattering technique.It is based on Raman Effect, i.e., frequency of a small fraction of scattered radiation is different from frequency of monochromatic incident radiation.

Scanning Electron Microscopy
SEM microscopes produce images of a sample by scanning it with a focused beam of electrons.The electrons interact with atoms in the sample, producing various signals that can be detected and that contain information about the sample's surface topography and composition.

Sorption microbalance
This balance allows weighing over time of small samples, with high accuracy.It integrates precise computer-control and measurement of mass change, pressure and temperature to enable fully automatic and reproducible determination of gas sorption-desorption isotherms and isobars in diverse operating conditions: controlled relative humidity, gas composition, temperature, pressure.

Thermogravimetric Analyses
This is a method of thermal analysis in which changes in physical and chemical properties of materials are measured as a function of increasing temperature, or as a function of time.TGA can provide information about physical phenomena, such as second-order phase transitions, including vaporization, sublimation, absorption, adsorption, and desorption.





